Problem
Find Your Ford connects dealers and customers for used car sales across multiple states.
Despite regular traffic, the site suffered from high bounce rates and low engagement. With leadership requiring quick results to justify further investment, the team needed to rapidly identify and prioritize features that would improve user retention.
The situation called for Lean Experiment, a quick, low-risk approach to validate assumptions and gather user insights through a build-measure-learn approach focused on rapid iteration.
Step 0: Discovery
The team kicked off discovery by running
1) Un-moderated usability testing with 9 participants using usertesting.com
2) In-person user interviews with 8 participants recruited through social media
3) A thorough competitor study
The following insights were revealed.
Excessive emphasis on dealers, creating the perception that Ford was prioritizing dealer business over customer needs.
Not enough tools to support user’s decision-making, such as warranty information and vehicle history, etc.
Missed opportunity promoting a ‘guaranteed’ hassle-free experience. Competitor sites offered features like return policies and vehicle delivery options.
Step 1: Hypothesis
Instead of re-hashing the entire website, the team came up with top 2 hypotheses.
1) Hypothesis 1 - Adding a finance calculator for each vehicle will help a prospective customer determine monthly payments and the total cost of auto loan, providing them with a crucial decision making tool.
The team identified an API that can be integrated with the existing site without having to build one.
2) Hypothesis 2 - Allowing users to bookmark vehicles for comparison will support their decision making process of narrowing down options by cost and features.
Bookmarking will ensure engagement.
Step 2: Experiment
The visiting traffic was split into A/B versions of the website.
Version A was the original website with no change
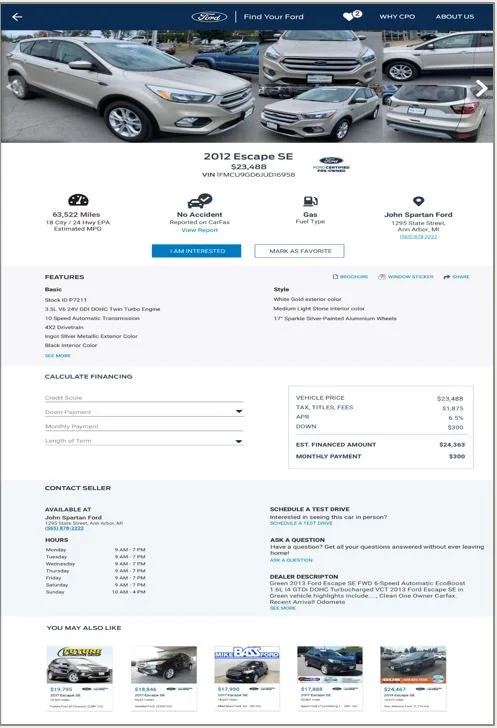
Version B included
A basic finance calculator
Ability to bookmark or favorite a vehicle for comparison
‘You may also like’ option to view similar vehicles (by showing vehicles of the same model or price range).
Version A
Version B
Scope
Experiment ran only for Dearborn region for a period of 2-3 weeks.
Step 3: Collect metrics
The site saw more than 100% increase in the number of visitors from 194 unique visits to 416 unique visits per day.
Summary
The Lean experiment passed the hypotheses and gave the team the confidence that the proposed design change would lead to positive improvements on the site. As the next step, the team persevered and looked for newer feedback to iterate the product.
Failing the hypothesis would have been an important learning as well. Failing is an opportunity to pivot to another solution.
Pivoting often leads to re-defining new hypotheses. Failing sometimes highlight wrong assumptions around the core user problem warranting another round of user research and lean experiments.